Adipose Tissue: Loose Connective Tissue
|
|
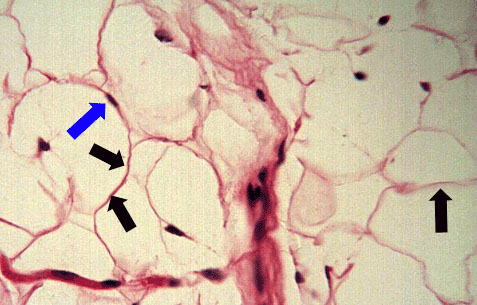
Adipose tissue is composed of cells called adipocytes. The adipocytes contain a very large fat-containing vacuole. This gives the cell the appearance of being empty. The nucleus is visible and usually appears squashed up against the plasma membrane. There is little matrix to this tissue.
Adipose tissue or fat is found just about everywhere, in your eyelids, around your organs, beneath your skin, behind your eyeballs, everywhere..... Adipose tissue plays an important role in protecting and cushioning parts of the body. It serves as an energy reserve and as a thermal insulator.
The photomicrograph to the right is adipose tissue. Notice the big empty-appearing adipocytes. The blue arrow is pointing to an adipocyte nucleus. The black arrows are pointing to the plasma membranes of the cells.
Reticular Tissue: Loose Connective Tissue
|
|
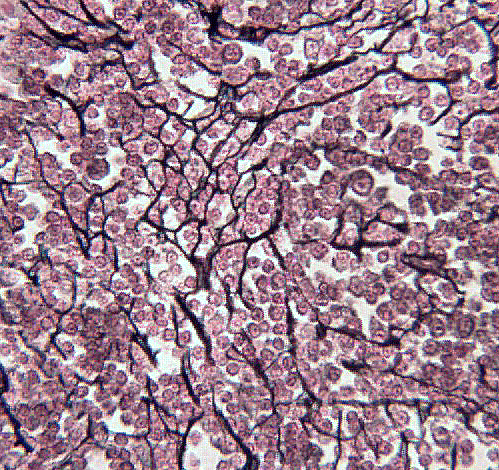
Reticular tissue is composed of a loose ground substance with distinctive reticular fibers. The reticular fibers stain black and blood cells (lymphocytes) are the predominant cell type. The reticular fibers provide a loose, flexible scaffold on which the cells rest. Reticular tissue is associated with lymphoid tissue like, lymph nodes.
In the photomicrograph to the right the reticular fibers are evident as dark black lines. The cells associated with the fibers are lymphocytes.